Most of them are outdated, but provide historical design context.
They are not user documentation and should not be treated as such.
Documentation is available here.
Supervdsm service
General
Supervdsm is responsible for all privileged operations. Currently Supervdsm is managed (started and restarted) by unprivileged process ‘vdsm’ and vdsm starts up by init service manager. To perform that, Vdsm process runs privileged operations, manage process that runs as root, and communicate with it by external UDS. All that leads to races between new and old instances of the process. Aim of this feature is to get Vdsm to be a pure unprivileged daemon and simplify the handling of crashes and re-establish communication between Vdsm and Supervdsm after failures.
Owner
- Name: lvroyce (Royce Lv)
- Name: ybronhei (Yaniv Bronheim)
- Email: lvroyce@linux.vnet.ibm.com
Background - History until 3.3
- current solution
- Vdsm daemon script starts vdsm with user “vdsm”
- Vdsm process launches supervdsm process when it is not running by sudo command
- Vdsm tries to send uds packets to supervdsm to establish communication
- When authentication error is raised, vdsm tries to re-launch (kill old instance and initiate new one)
- When vdsm crashes, supervdsm distinguish it and kill itself automatically, next vdsm instance starts new supervdsm process
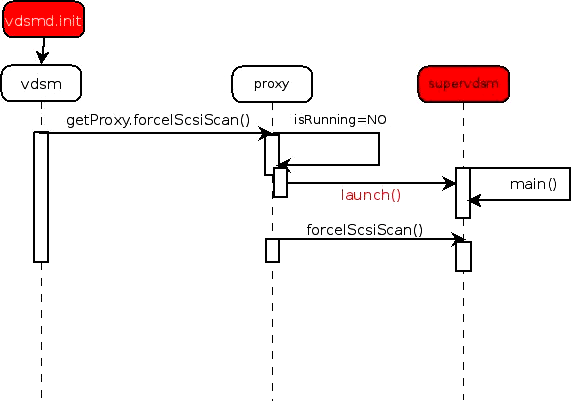
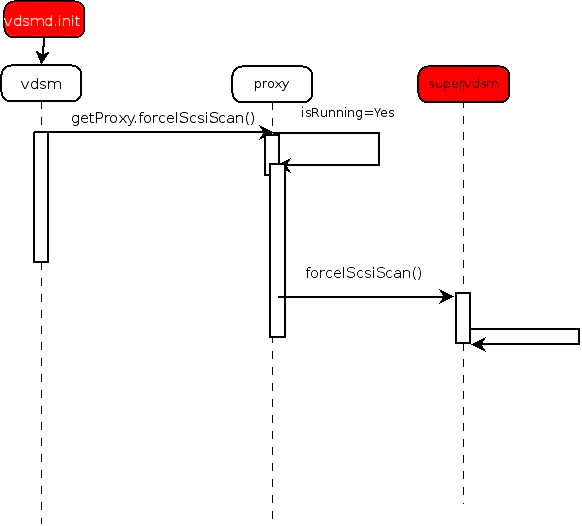
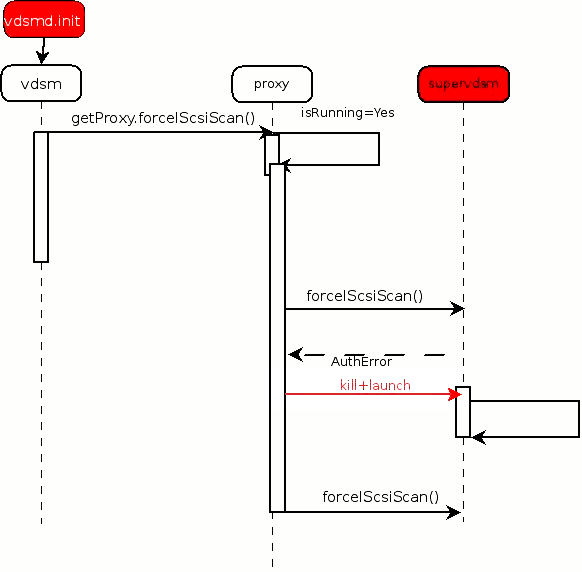
- Current flow errors
- Unprivileged vdsm and proxy need to call previleged “sudo launch” and “sudo kill”
- Redundant key between vdsm and supervdsm as they are parent and child
- Error handling cause races between old and new instance of supervdsm and vdsm
- Last updated: ,
Proposed changes
- Proposal A:patch for proposal A
- Vdsm init script starts vdsm as root
- Vdsm forks supervdsm server and then drop privilege
- When vdsm exits, supervdsm probe vdsm heart beat stop and exit
- Vdsm call supervdsm may discover supervdsm server exit, vdsm will exit itself and restart
- Proposal B:patch for proposal B
- Vdsm init script starts supervdsm as root
- Supervdsm forks vdsm as child process
- When vdsm dies, supervdsm kill itself and start over again
- When supervdsm, vdsm distinguish that and kill itself
- proposal C:patch for proposal C -> Selected solution.
- Vdsmd.init starts vdsm as vdsm user
- Supervdsmd.init starts supervdsm as root
- Both services are managed by service manager and restart after a crash.
- No need to handle broken connection. When supervdsm or vdsm fails to start an automatically restart takes care of establishing recommunication.
Exception flows to consider
- Exception flows:
- One of Supervdsm server export function raise error
- Expected result: Raise to proxy caller, supervdsm restarts automatically without trying to call the same function again. The proxy caller should handle exceptions specifically.
- Supervdsm main thread died during a call or before call
- Expected result: Raise to proxy caller related exception. Supervdsm proxy caller should handle exceptions specifically.
- Vdsm crash
- supervdsm stays up and vdsm re-establish communication to supervdsm socket after restart.
Proposal comparison
- Exception flows need attention:
- First launch
- A: Supervdsm server process lauched by priviledged vdsm, then vdsm drop priviledge
- B: Supervdsm server process lauched by service manager
- C: Supervdsm server process launched by service manager
- One of supervdsm server export function raise error
- A: Raise to Proxy Caller
- B: Raise to Proxy Calller
- C: Raise to Proxy Calller
- Supervdsm main thread killed when calling
- A: Discover when call return EOFError and then restart
- B: Vdsmd as supervdsm’s child should kill itself when receive EOFError
- C: Services manager restarts supervdsm. Caller should handle the returned exception.
- Supervdsm main thread killed before call
- A: Discover when “isRunning” raise error, then restart
- B: Vdsmd as supervdsm’s child should be killed when next time supervdsm start, or vdsmd also has a heart beat scheme for super vdsm
- C: Supervdsmd restarts supervdsm
- Supervdsm server thread killed(not started) before call
- A: Connect error, restart
- B: Supervdsm restart itself
- C: Service manager restarts Supervdsm.
- Vdsm process died
- A: Supervdsm has heart beat for Vdsm to kill itself
- B: Supervdsm joined Vdsm and restart all over
- C: Service manager restarts Vdsm.
As we can see from the above, proposal B will involve more complex logic when supervdsm died, vdsm will probe its heart beat or supervdsm should kill vdsm for next time, but vdsm still in the middle of some operations, possible inconsistent situation will happen. Proposal C is intuitive, easier, and less complex than both A and B proposals. The main odd is that every code update of vdsm we need restart both services, as they both share same code.
Benefit to oVirt
- Clean vdsm priviledge usage
- Clean and stable vdsm/supervdsm exception flow and races