Most of them are outdated, but provide historical design context.
They are not user documentation and should not be treated as such.
Documentation is available here.
Hot plug cpu
Summary
This feature allows you to hot plug CPUs to a running virtual machine from the oVirt engine user interface and REST API.
Owner
- Name: Roy Golan
- Email: rgolan@redhat.com
Current status
- phase 1 (i.e all content in this wiki) - Done
- phase 2 - Hot_plug_cpu#Phase_2 desgin stage
- limitations: unplug isn’t supported fully due to libvirt’s Bug #1017858
Detailed Description
Historically, CPU and memory hot add and remove capabilities were thought of as server hardware RAS features. However, the concepts of CPU and memory hot add and remove are both common and necessary for Virtualized environments. Virtual CPUs and virtual memory assigned to a virtual machine (VM) need to be be added or removed from a running guest in order to meet either the workload’s demands or to maintain the SLA associated with the workload. It is also desired for the rapid reconfiguration of a guest once a workload has been completed or migrated and an administrator wants to reconfigure the VM without having to re-boot the VM.
Benefit to oVirt
This feature enables the following powerful use cases:
- Admins can ensure customer’s SLA are being met
- Spare hardware can be effectively used - it’s common to see systems overdimentioned x3 for an average max load
- System hardware can be dynamic scaled vertically, down or up, in accordance with your needs without restarting the virtual machine
Detailed Design
Client Usage
The term plug/unplug CPUs is simpler from the user POV. The user just needs to set the desired number of sockets he needs. I.e we support a number which is the multiplication of the Cores per sockets and sockets.
All of this means that the user can now simply change the number of sockets of a running VM while its status is UP.
This would trigger a call to VDSM to setNumberOfCpus(vmId, num).
There is no notion of plug/unplug.
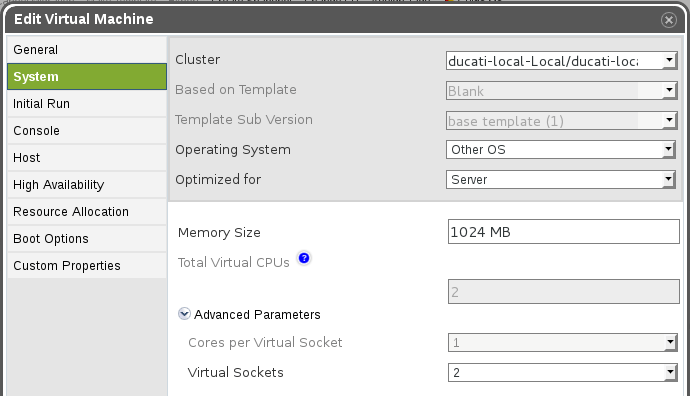
UI
See that “Sockets” text input is editable while the VM is UP (its editable only when UP or DOWN statuses)
REST
This is a typical update to a VM resource. The number of sockets is changed to 2. This will hotplug 1 more CPU to the machine.
$ cat hotplug-cpu.xml
<vm>
<cpu>
<topology sockets="2" cores="1"></topology>
</cpu>
</vm>
curl -X PUT \
--user user@domain:pass \
-H "Content-Type:application/xml" \
-d@hotplug-cpu.xml http://localhost:8080/ovirt-engine/api/vms/${vmId}
Engine
Engine must allow updates to the number of sockets field while the VM is up. When calling the UpdateVmCommand, we will check
if the current number is different then the stored number of sockets. if it is we then call VDSM setNumberOfCpus(vmId, num).
If we returned with no error, the new number of CPUs is stored into db. The engine view of the actual vCpus of this machine is now syncronized.
A pre-condition for adding more CPUs is that a VM has a MAX_VCPUS set in its xml.
This means we have to start the VM with some configured maximum.
This number doesn’t affect any reosurce allocation on the VM itself.
Till today the MAX_VCPUS was equal to the number of CPUs the VM started with.
So its impossible to hot plug more CPUs to machines that started < 3.4 (i.e setup upgraded and the machines stayed UP)
pseudo-code for building a VM xml we send to VDSM
if (hot plug is supported for this compat version) {
smp = ConfigValues.MaxNumOfVmCpus
}
Update Vm Command - Error handling
The API to hot plug CPU is using UpdateVmCommand.
Essentially if there is a change in topology a child Command HotSetNumberOfCpus will be called.
The call to the child command fails atomically and it shall NOT abort the parent UpdateVmCommand.
e.g - we want to update a running’s VM desription and to hotplug 1 more cpu
- the updated values are desctiption and numberOfSockets
- UpdateVmCommad saves the descitption to DB
- HostSetNumberOfCpus is called with new number of sockets but fails
- UpdateVmCommand check for the failure and outputs and AuditLog
- UpdateVmCommand terminates and commit changes to DB with the new description only. the old number of sockets remains unchanged
changes
| Component | requirement | completed |
|---|---|---|
| Engine | UpdateVmCommand permits number of cpus change while VM is running | Done |
| Engine | UpdateVmCommand canDo fail if # of cpus is not supported on host (config value?, get the actual number from caps?) | 0 |
| Engine | UpdateVmCommand send setNumberOfCpus verb when cpus changes | Done |
| Engine | UpdateVmCommand stores the new number of CPUs only if the call to setNumberOfCpus succeeded | Done |
| Engine - osinfo | create configuration for plug/unplug | not clear which OSs we block/allow - PPC is blocked entirely |
| Engine | create informative Audit log when setNumberOfCpus fails | Done |
| VDSM | create new verb ‘setNumberOfCpus’. it would be used for both plug/unplug cpus | Done |
| VDSM | in vm.py, bind the verb to an underling call to libvirt’s setVcpus | Done |
| VDSM | call before/after hooks for plug/unplug to enable various method for onlining the CPU at the guest OS | Done |
check list
| Component | check | completed |
|---|---|---|
| VDSM | check migration of a VM that was hotplugged with cpus and re-migrated it (not sure changes needed) |
Dependencies / Related Features
- setNumOfCpus –guest (using qemu guest agent for plug/unplug)
There is no direct dependency on QEMU’s agent. But for the sake of documenting any detail we have, its worth mentioning that
libvirt’s setNumOfCpus –guest will use the guest agent to offline/online the requested cpu instead of a real plug/unplug
i.e that the as for RHEL, the guest alone handles the plug/unplug without the need of the agent to do the underling job.
for more details see comment 11 on Bug #1017858
Guest OS Support Matrix
| OS | Version | Arch | Plug | Unplug |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.3 | x86 | + | - | |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.5 | x86 | + | + | |
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 | All | x86 | - | - |
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 | All | x64 | - | - |
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 | All | x86 | - | - |
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 | Standard, Enterprise | x64 | Reboot Required | Reboot Required |
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 | Datacenter | x64 | + | ? |
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 | All | x86 | - | - |
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 | Standard, Enterprise | x64 | Reboot Required | Reboot Required |
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 | Datacenter | x64 | + | ? |
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 | All | x64 | + | ? |
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 | All | x64 | + | ? |
| Microsoft Windows 7 | All | x86 | - | - |
| Microsoft Windows 7 | Starter, Home, Home Premium, Professional | x64 | Reboot Required | Reboot Required |
| Microsoft Windows 7 | Enterprise, Ultimate | x64 | + | ? |
| Microsoft Windows 8.x | All | x86 | + | ? |
| Microsoft Windows 8.x | All | x64 | + | ? |
Documentation / External references
Open Issues
Possible error when migrating a VM which its max cpu is lower than what currently in <vcpu current=n>m</vcpu>
The current VM on the source has n cpus attached and need m maximum to be able to online more. if m1 is the max cores on the the source H1 host and m2 is the maximum on destination host H2 if m1 > m2 the underlying migration should fail?
Possible CPU pinning problems
if we have cpu pinning for cpu 1-4 and we start the VM with 4 CPU and then we offline 2 CPUs and then we online them back - is the pinning kept?
hook support
hook support is provided to solve potential problems with online/offline the cpu after the actual addition to the VM system. Its not clear if some linux versions will have the cpu added but offline in the system so the hook is to cover the gap.
/usr/libexec/vdsm/hooks/before_set_num_of_cpus/usr/libexec/vdsm/hooks/after_set_num_of_cpus
Phase 2
Due to libvirt bug on unplug the engine has an inconsistent view of the amount of CPUs the VM has. i.e after unplugging 4 vcpus to 2 vcpus the VM entity in DB has 4 and in qemu process it will decrease to 2
status: in progress related bugs: 1077515
block Unplug
- block unplug operation (based on static vm cpu count)
- engine can do
- UI grey-out lower values
- vdc_option for unplug=false in 3.4 till otherwise be it supported.
- add it to engine-config so its exposed to admins
notify VDSM Guest Agent
- call vga (vdsm guest agent) setNumCpus(num:int)
- log if unsupported operation on guest
- call setnumofCpu will trigger a refresh
report topology
-
report the CPU topology under VM subtab
TODO scketch it
-
format of the topology (Vinzenz please fill in)
note: VDSM-guest-agent work for reporting this is already in progress - http://gerrit.ovirt.org/23268
Testing
- how to check the guest CPUs - LINUX
lscpu -e -a
TODO - format the tests
- CPU hot unplug \ CPU loaded
- Set up
- Actions
- Have a VM with 2 CPUs with 100 % utilization - try to hot unplug 1 CPU.
- Hot plug 1 CPU.
- Expected Results
- See how the OS handle the requiest in such case.
- As the unplug process should take time, interesting to see, how the OS respose to the hot plug.
- Breakdown
- Negative test - Add CPU above max
- Set up
- Actions
- Update VM number of CPUs, to a value greater than host capabilities, while VM is running.
(Check what is the maximum number of CPUs, supported on host by getVdsCaps on host).
-
- Expected Results
CanDoActionfail
- Breakdown
- Expected Results
- Negative test - CPU hot plug single CPU
- Set up
- Actions
- For a VM with 1 CPU, try to run CPU hot unplug.
- Expected Results
- Expect
CanDoAction, since 1 CPU is the minimum.
- Expect
- Breakdown
- Negative test - CPU hot plug, before qemu-kvm updated
- Set up
Background:
When running CPU hot plug/unlug, the engine gets acked from qemu-kvm side, even before CPU count has actually updated in qemu-kvm. Therefore, user is reflected that the CPU number was already updated. At this point of time, user can run a 2nd CPU plug/hotplug. Actions
-
Add CPUs to a running VM (2->4, for example)
-
Remove CPU (4->2, for example), right after the hot add (step 1).
To see the number of CPUs is yet increased, see test plan documentation on how to do so on guest.
Expected Results
-
Should fail nicely. Breakdown [338998] Negative test - CPU pinning Set up Actions
-
Have a VM with cpu pinning defined to 3 first CPUs, in ordered manner. Start the VM with 4 CPUs.
-
Hot unplug 2 CPUs. (update number of CPUs from 4 to 2), while VM is running.
-
Have a VM with cpu pinning defined to 2 CPUs, and CPU pinning to #2, & #3. Hot plug 2 CPUS, and then hot unplug 2 CPUs. Expected Results
-
Should fail, cpu pinning should block this change.
-
Should fail. Libvirt should block this upon cpu pinning. Breakdown [337910] Negative test - Hot plug during migration Set up Actions
-
Try to CPU hot-plug (add or reduce CPUs) during VM migration. Expected Results
-
Failure message or can do action (no exceptions in the log). Breakdown [338661] Positive test - CPU hot plug & unplug toggle Set up Actions
-
CPU hot plug & unplug toggle several times. Expected Results
-
CPU number should get updated as configured on guest. Breakdown [337912] Positive test - CPU pinning Set up Actions
-
Have a VM with cpu pinning defined to 3 first CPUs, in ordered manner. Start the VM with 4 CPUs.
-
Hot unplug 1 CPU (update number of CPUs from 4 to 3), while VM is running. Expected Results
-
Should be successful.
-
Should be successful. Breakdown [338718] Positive test - CPU thread Set up Actions
-
CPU hot plug 2->4, without cluster CPU thread activated.
-
Also consider here SLA cluster level hypertherding, and in case it is active, the number of CPUs = Hyperthreding (CPU Thred) * Cores * Sockets Expected Results
-
See that the maximum allowed number of CPUs = CPU cores * CPU sockets.
-
See that maximum allowed number of CPUs = CPU cores * CPU sockets * CPU thread Breakdown [337907] Positive test - Hot Add\Remove CPUs Set up Actions
-
Start A VM with 2 CPUs, 2 cores each .
-
Update number of CPUs to 4, while VM is running.
-
Update number of CPUs to 2, while VM is running.
Expected Results
-
a. See that the number of CPUs updated correctly & successfully in UI and REST.
b. Verify CPU count = 4, by checking it on guest (see test plan documentaion for how to). (it may take some time to reach the correct CPU count.) -
Same as 2, expect CPU count =2. Breakdown [337909] Positive test - Migrate VM hot plugged with CPUs Set up
Require 2 hosts for migration. Actions
-
CPU hotplug add: While VM is running, add more CPUs, for example, for a VM with 2 CPUs, update to 4 CPUs.
-
Migrate the VM.
-
Migrate VM back to original host.
-
Repeat 1-3 for CPU hot unplug of 4->2.
-
Have 2 VMs, each on a separate host. CPU hot plug on VM 1 from 2->4. CPU hot unplug on VM 2 from 4->2. Migrate concurretly VM1 and VM2. Expected Results
-
CPU hot plug should be successful. Check on guest by running ‘lscpu’ that the CPU number has been updated to 4.
-
Migration should succeed. Check on guest (see test plan documentaion for how to), that the CPU number = 4 .
-
Same as 2.
-
Expect same results as 1-3
-
After migrations, the CPU number on guest should be as configured. Breakdown [337913] Positive test - vdsm hooks Set up
vdsm hooks - vdsm call before/after hooks for plug/unplug to enable various method for onlining the CPU at the guest OS Actions
- Fill on host, where VM is running, these vdsm hook files:
a. /usr/libexec/vdsm/hooks/before_set_num_of_cpu, for example, with this content: echo “running before_set_num_of_cpu”
b. /usr/libexec/vdsm/hooks/after_set_num_of_cpu, for example, with this content: echo “running after_set_num_of_cpu”
-
Plug: Add CPUs to a VM, for example, 2->4.
-
Unplug: Reduce CPUs to a VM, for example, 4->2.
Expected Results
-
-
Check on guest that CPU number was updated (see test plan documentaion for how to).
- Verify that both hook files run & exceuted.
-
- Same as 2, Except due to bug 1017858 , the after script will not be called till resolved. Breakdown [339000] System test Set up
Have a VM with a single CPU, which is fully utilized Actions
-
. Hot plug CPU 1 -> 2. Expected Results
-
Check adaptation of the OS of the CPU change: Verify indeed the hot plug indeed improve the performance, and the 2nd CPU is used to balance the load.