Chapter 6: Deploying a Single Node oVirt and Gluster Hyperconverged
Pre-requisites
-
A single host with Enterprise Linux 8 or oVirt Node. Refer Enterprise Linux Hosts or oVirt Nodes
-
You must have at least 2 interfaces on the host, so that the frontend and backend traffic can be separated out. Having only one network will cause the engine monitoring, client traffic, gluster I/O traffic to all run together and interfere each other. To segregate the backend network, the gluster cluster is formed using the backend network addresses, and the nodes are added to the engine using the frontend network address.
-
You must have a fully qualified domain name prepared for your Engine and the host. Forward and reverse lookup records must both be set in the DNS. The Engine should use the same subnet as the management network.
-
You must have configured passwordless ssh between the host to itself as ansible roles need to remotely execute commands is a pre-requisite. Follow below steps to configure this.
# ssh-keygen # ssh-copy-id root@<host-address>
Deploying on Enterprise Linux Hosts
Installing the Required Packages
Installing the packages on the host
-
Subscribe to ovirt repos from http://resources.ovirt.org/pub/yum-repo/ For instance, to subscribe to oVirt 4.4 repo,
# yum install http://resources.ovirt.org/pub/yum-repo/ovirt-release44.rpm -
Install gluster-ansible-roles and cockpit-ovirt that will provide a UI for the installation of Hosted Engine. gluster-ansible project provides Ansible roles to deploy, configure, and maintain GlusterFS clusters.The roles are classified into following categories, which will have sub-roles (if necessary) for specific task, which will be explained in detail in their respective repositories.
gluster.infra - helps the user to get started in deploying GlusterFS filesystem gluster.cluster - helps the user to set up a GlusterFS cluster, manage gluster volumes and peer operations. gluster.features - implements GlusterFS usecases: nfs_ganesha, gluster_hc, ctdb, geo_replication. gluster.repositories - helps user to register to RHSM and subscribe to repositories gluster.maintenance - helps user to replace nodes and other maintenance activities. vdsm-gluster is used to manage gluster from oVirt, and pulls in all the required gluster dependencies. Install the oVirt Engine Virtual Appliance package for the Engine virtual machine installation.
# yum install gluster-ansible-roles cockpit-ovirt-dashboard vdsm-gluster ovirt-engine-appliance
Deploying on oVirt Node based Hosts
oVirt Node contains all the required packages to set up the hyperconverged environment. Refer to oVirt Nodes for instructions on installing oVirt Node on the host. You can proceed to setting up the hyperconverged environment if you have an oVirt Node based host.
Setting up the hyperconverged environment
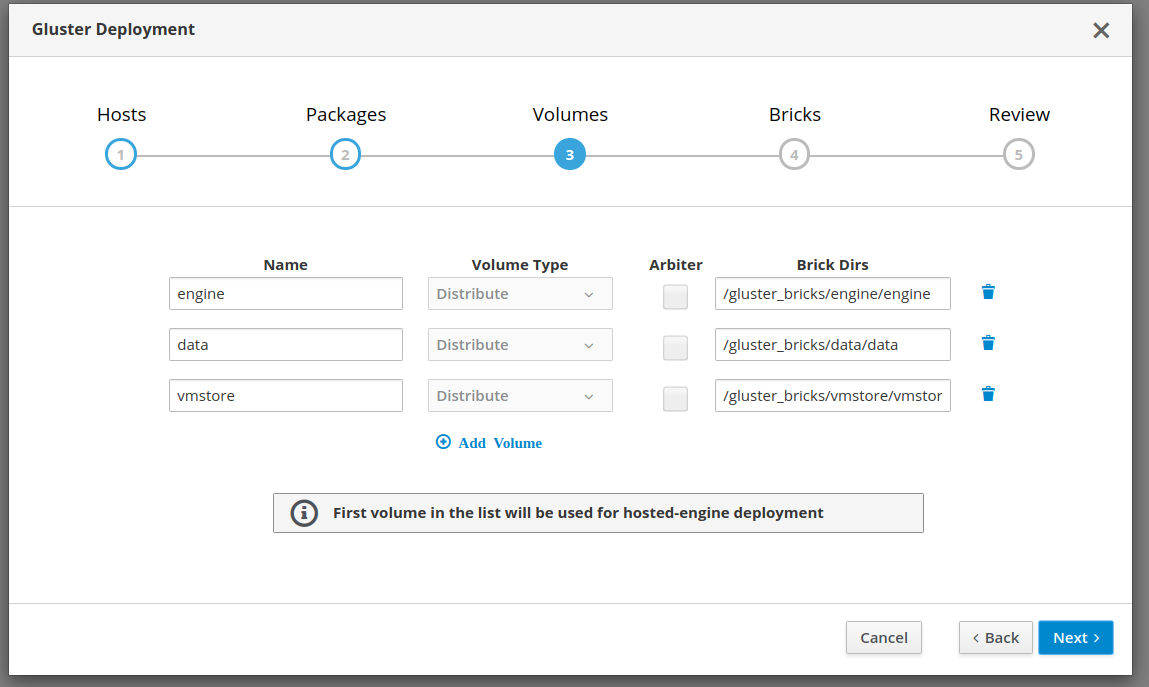
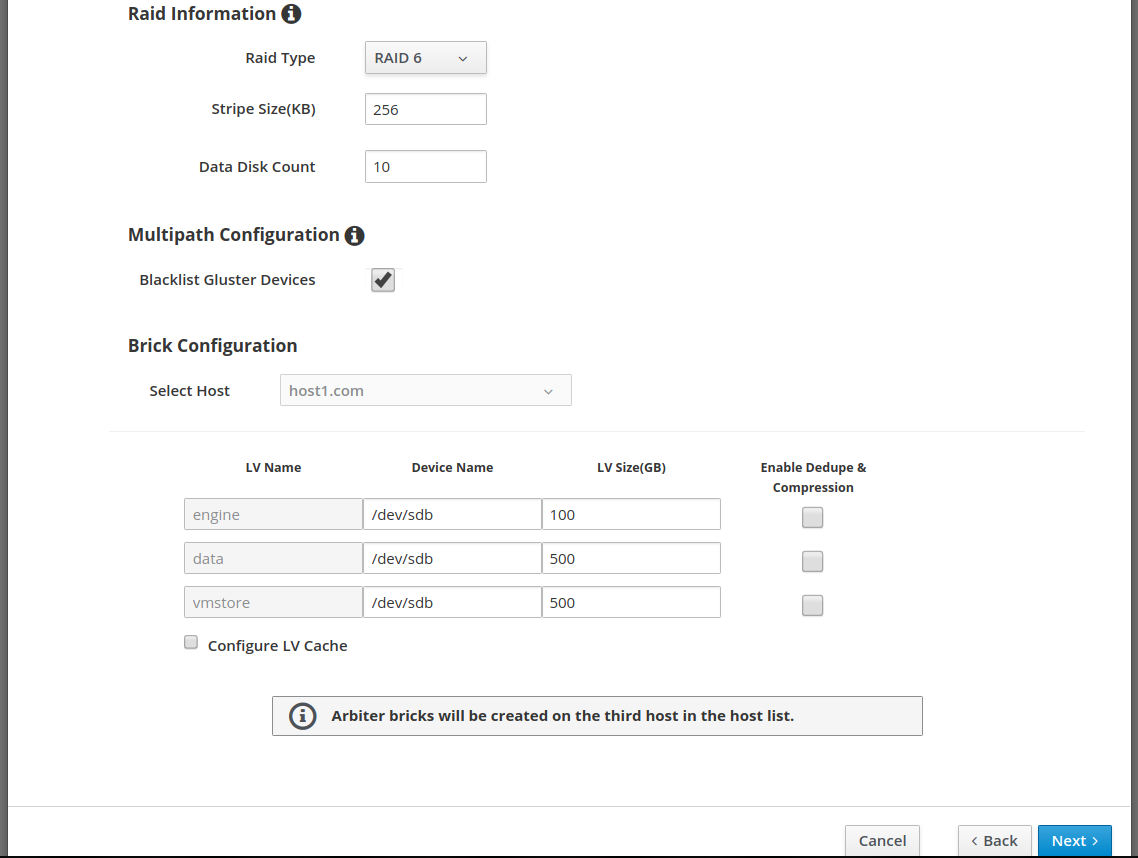
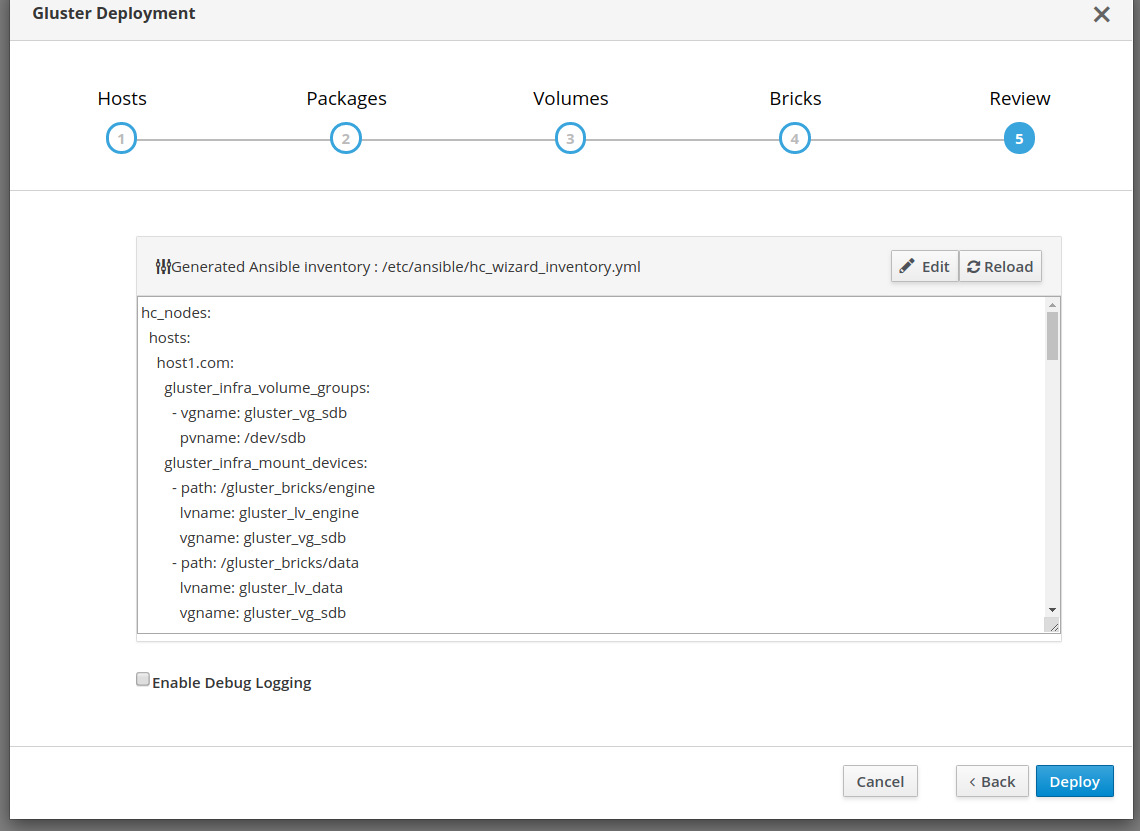
Installing and setting up gluster volume
Gluster volumes need to be created first prior to the Hosted Engine installation flow. One of the volumes that’s created is used to host the Hosted Engine VM. Use the Cockpit UI to setup single node deployment.
-
Log into the Web Console Browse to the the Web Console management interface of the first hyperconverged host, for example, https://node1.example.com:9090/, and log in with the root/similar super user credentials.
-
Start the deployment wizard
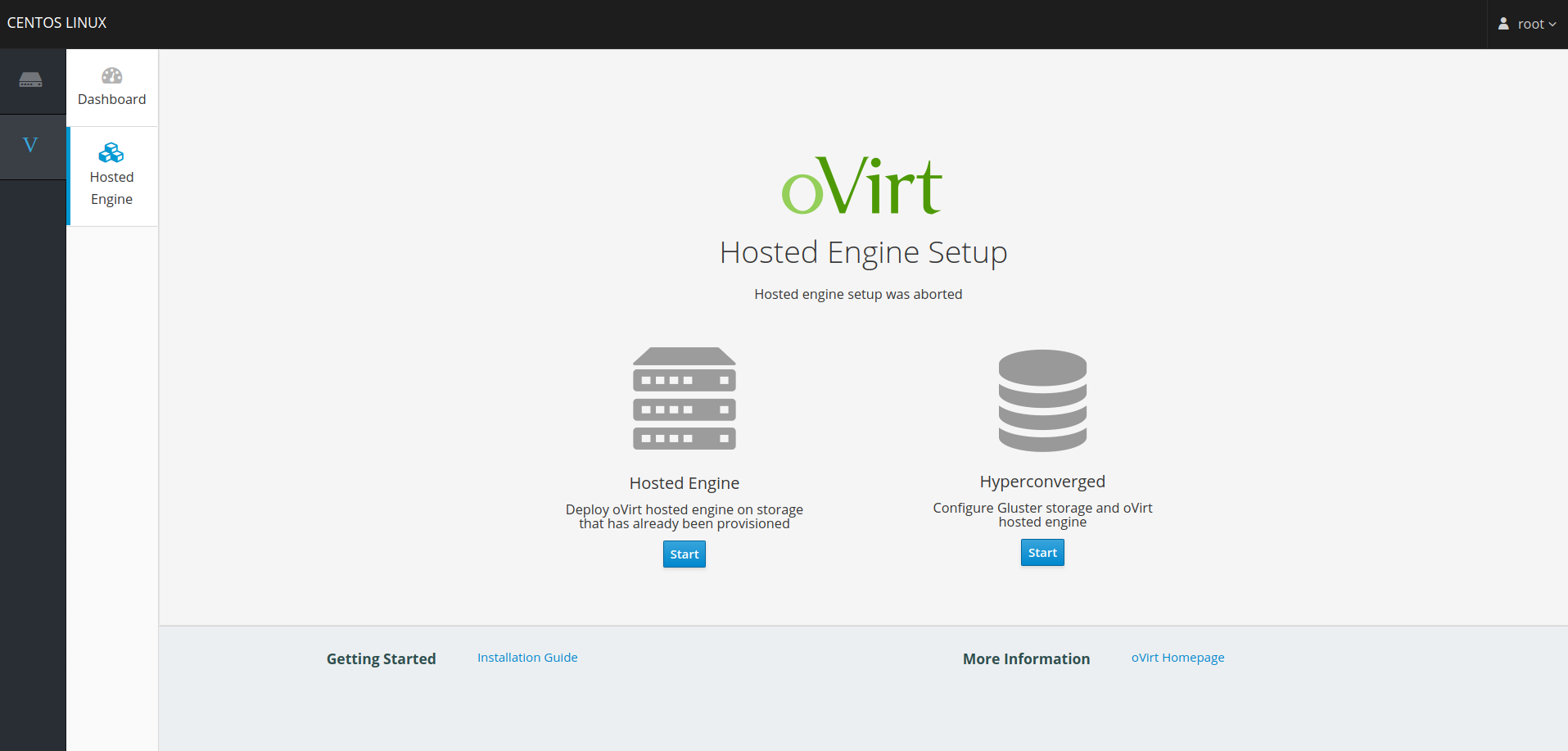
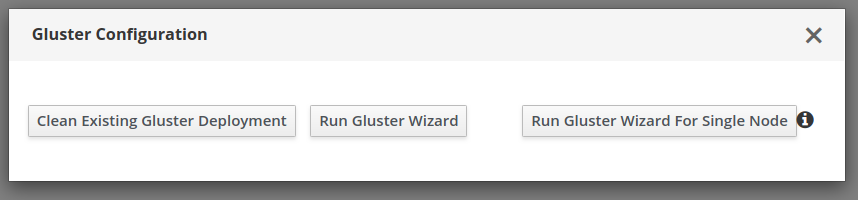
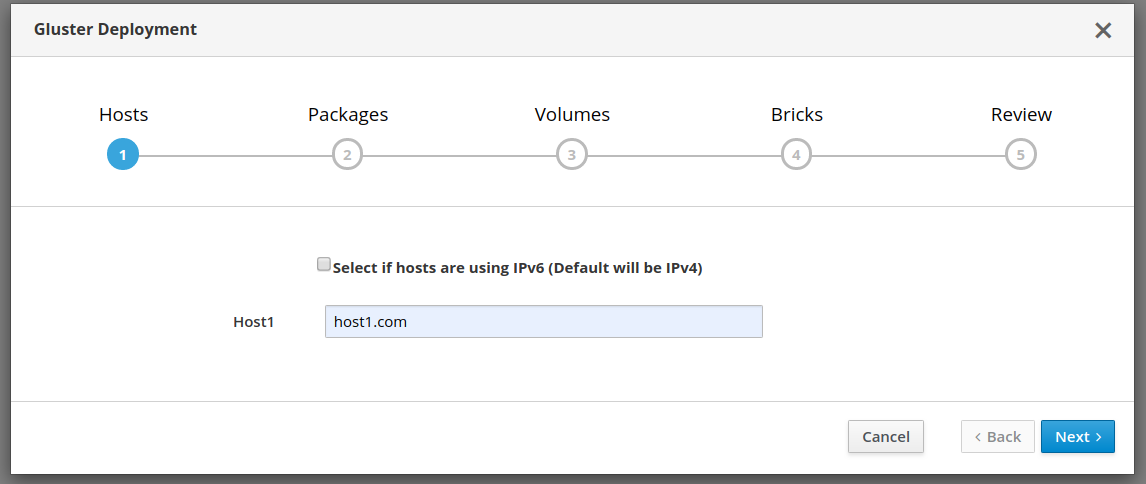
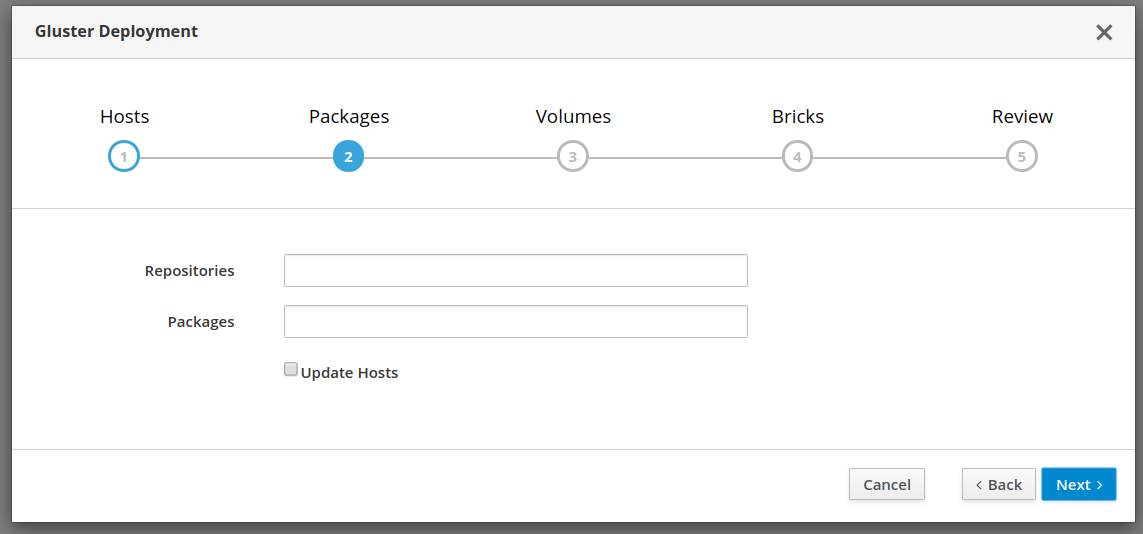
Setting up Hosted Engine
Use the Ansible based installation flow of Hosted Engine to set up oVirt within a virtual machine. The storage details should be provided as type: glusterfs and connection path as: <hostname>:/engine (Replace hostname with address of host on which installation is carried out)