Most of them are outdated, but provide historical design context.
They are not user documentation and should not be treated as such.
Documentation is available here.
Self Hosted Engine
Summary
The ability to run the Engine as a VM on the hosts that are managed by this Engine, in an HA configuration, when the Engine VM can start on any of the hosts.
Owner
- Featue Owner: Sean Cohen: scohen (scohen)
- Email: scohen@redhat.com
- Engine Component owner: Sandro Bonazzola
- Email: sbonazzo@redhat.com
- VSDM Component owner:
Current status
- Initial POC devel
Detailed Description
This feature will deal with two main issues:
- The deployment of an Engine as a VM into a fresh setup.
- HA for the Engine VM needs to be managed by the hosts and not the Engine.
Benefit to oVirt
- This will allow us to deploy less hardware (with the Engine not requiring a separate machine)
- We will be capable of providing HA for the Engine out of the box, instead of using a separate cluster in order to make the Engine HA.
- This operational mode will attract users already familiar with it from other virt platforms.
Requirements
- New installation should be simple and guided.
- A user will start with a single hypervisor host (full host OS or ovirt-node support is planned for 3.5), that can access shared storage, and after the setup, will be able to access the Engine webadmin UI in order to add mode hosts, clusters, SDs etc.
- The engine should be able to start on any of the hosts it manages, provided the hosts have the hosted engine addons installed.
- The engine should be highly available, and be able to tolerate host, network and storage failures.
- An ability to define priorities for hosting the engine is a “nice to have”.
- The host currently running the engine should report additional resources used, just like we reserve an extra CPU for the SPM, and compensate for that.
- Some resources (especially RAM) should be reserved on one or two nodes in the cluster, in case the engine VM has to migrate over
- ovirt-node should have a TUI for the initial deployment and configuration of the Engine VM
- Should support importing an existing installed engine ovf as installation media
Detailed Description
RPM level
- package should require vdsm enabling the host to be an hypervisor
- package should require cli/sdk to comunicate with engine
UI - first host deployment
Here is an example of a first host deployment:
# yum install ovirt-hosted-engine-setup
# hosted-engine --deploy
[ INFO ] Stage: Initializing
Continuing will configure this host for serving as hypervisor and create a VM where oVirt Engine will be installed afterwards.
Are you sure you want to continue? (Yes, No)[Yes]: yes
It has been detected that this program is executed through an SSH connection without using screen.
Continuing with the installation may lead to broken installation if the network connection fails.
It is highly recommended to abort the installation and run it inside a screen session.
Do you want to continue anyway? (Yes, No)[No]: yes
[ INFO ] Generating a temporary VNC password.
[ INFO ] Stage: Environment setup
Configuration files: []
Log file: /var/log/ovirt-hosted-engine-setup/ovirt-hosted-engine-setup-20131121151103.log
Version: otopi-1.1.1 (otopi-1.1.1-1.el6ev)
[ INFO ] Hardware supports virtualization
[ INFO ] Bridge rhevm already created
[ INFO ] Stage: Environment packages setup
[ INFO ] Stage: Programs detection
[ INFO ] Stage: Environment setup
[ INFO ] Stage: Environment customization
--== STORAGE CONFIGURATION ==--
During customization use CTRL-D to abort.
Please specify the full shared storage connection path to use (example: host:/path): myhost.home:/export
[ INFO ] Installing on first host
Please provide storage domain name [hosted_storage]:
Local storage datacenter name [hosted_datacenter]:
--== SYSTEM CONFIGURATION ==--
--== NETWORK CONFIGURATION ==--
iptables was detected on your computer, do you wish setup to configure it? (Yes, No)[Yes]:
Please indicate a pingable gateway IP address: 10.1.1.1
--== VM CONFIGURATION ==--
Please specify the device to boot the VM from (cdrom, disk, pxe) [cdrom]: pxe
The following CPU types are supported by this host:
- model_Conroe: Intel Conroe Family
Please specify the CPU type to be used by the VM [model_Conroe]:
Please specify the number of virtual CPUs for the VM [Defaults to minimum requirement: 2]:
Please specify the disk size of the VM in GB [Defaults to minimum requirement: 25]:
Please specify the memory size of the VM in MB [Defaults to minimum requirement: 4096]:
Please specify the console type you would like to use to connect to the VM (vnc, spice) [vnc]:
--== HOSTED ENGINE CONFIGURATION ==--
Enter the name which will be used to identify this host inside the Administrator Portal [hosted_engine_1]:
Enter 'admin@internal' user password that will be used for accessing the Administrator Portal:
Confirm 'admin@internal' user password:
Please provide the FQDN for the engine you would like to use. This needs to match the FQDN that you will use for the engine installation within the VM: hosted-engine.home
[WARNING] Failed to resolve hosted-engine.home using DNS, it can be resolved only locally
Please provide the name of the SMTP server through which we will send notifications [localhost]:
Please provide the TCP port number of the SMTP server [25]:
Please provide the email address from which notifications will be sent [root@localhost]:
Please provide a comma-separated list of email addresses which will get notifications [root@localhost]:
[ INFO ] Stage: Setup validation
--== CONFIGURATION PREVIEW ==--
Engine FQDN : hosted-engine.home
Bridge name : rhevm
SSH daemon port : 22
Firewall manager : iptables
Gateway address : 10.1.1.1
Host name for web application : hosted_engine_1
Host ID : 1
Image size GB : 25
Storage connection : myhost.home:/export
Console type : vnc
Memory size MB : 4096
Boot type : pxe
Number of CPUs : 2
CPU Type : model_Conroe
Please confirm installation settings (Yes, No)[No]: yes
[ INFO ] Generating answer file '/etc/ovirt-hosted-engine/answers.conf'
[ INFO ] Stage: Transaction setup
[ INFO ] Stage: Misc configuration
[ INFO ] Stage: Package installation
[ INFO ] Stage: Misc configuration
[ INFO ] Configuring libvirt
[ INFO ] Generating VDSM certificates
[ INFO ] Configuring VDSM
[ INFO ] Starting vdsmd
[ INFO ] Waiting for VDSM hardware info
[ INFO ] Waiting for VDSM hardware info
[ INFO ] Creating Storage Domain
[ INFO ] Creating Storage Pool
[ INFO ] Connecting Storage Pool
[ INFO ] Verifying sanlock lockspace initialization
[ INFO ] Initializing sanlock lockspace
[ INFO ] Initializing sanlock metadata
[ INFO ] Creating VM Image
[ INFO ] Disconnecting Storage Pool
[ INFO ] Start monitoring domain
[ INFO ] Configuring VM
[ INFO ] Updating hosted-engine configuration
[ INFO ] Stage: Transaction commit
[ INFO ] Stage: Closing up
[ INFO ] Creating VM
You can now connect to the VM with the following command:
/usr/bin/remote-viewer vnc://localhost:5900
Use temporary password "1015iuUQ" to connect to vnc console.
Please note that in order to use remote-viewer you need to be able to run graphical applications.
This means that if you are using ssh you have to supply the -Y flag (enables trusted X11 forwarding).
Otherwise you can run the command from a terminal in your preferred desktop environment.
If you cannot run graphical applications you can connect to the graphic console from another host or connect to the console using the following command:
virsh -c qemu+tls://10.1.1.10/system console HostedEngine
If you need to reboot the VM you will need to start it manually using the command:
hosted-engine --vm-start
You can then set a temporary password using the command:
hosted-engine --add-console-password=`<password>
Please install the OS on the VM.
When the installation is completed reboot or shutdown the VM: the system will wait until then
Has the OS installation been completed successfully?
Answering no will allow you to reboot from the previously selected boot media. (Yes, No)[Yes]: yes
[ INFO ] Creating VM
You can now connect to the VM with the following command:
/usr/bin/remote-viewer vnc://localhost:5900
Use temporary password "1015iuUQ" to connect to vnc console.
Please note that in order to use remote-viewer you need to be able to run graphical applications.
This means that if you are using ssh you have to supply the -Y flag (enables trusted X11 forwarding).
Otherwise you can run the command from a terminal in your preferred desktop environment.
If you cannot run graphical applications you can connect to the graphic console from another host or connect to the console using the following command:
virsh -c qemu+tls://10.1.1.10/system console HostedEngine
If you need to reboot the VM you will need to start it manually using the command:
hosted-engine --vm-start
You can then set a temporary password using the command:
hosted-engine --add-console-password=`<password>
Please install the engine in the VM, hit enter when finished.
[ INFO ] Engine replied: DB Up!Welcome to Health Status!
[ INFO ] Waiting for the host to become operational in the engine. This may take several minutes...
[ INFO ] Still waiting for VDSM host to become operational...
[ INFO ] Still waiting for VDSM host to become operational...
[ INFO ] The VDSM Host is now operational
Please shutdown the VM allowing the system to launch it as a monitored service.
The system will wait until the VM is down.
[ INFO ] Enabling and starting HA services
Hosted Engine successfully set up
[ INFO ] Stage: Clean up
[ INFO ] Stage: Pre-termination
[ INFO ] Stage: Termination
Notes:
- Remember to setup the same hostname you specified as FQDN while you’re installing the OS on the VM.
-
If you want to install ovirt-engine-dwh and ovirt-engine-reports or update the engine after the deployment is completed , remember that you need to set the system in global maintenance using # hosted-engine –set-maintenance=global
because the engine service must be stopped during setup / upgrade operations.
UI - additional host deployment
Here is an example of deployment on an additional host:
# yum install ovirt-hosted-engine-setup
# hosted-engine --deploy
[ INFO ] Stage: Initializing
Continuing will configure this host for serving as hypervisor and create a VM where oVirt Engine will be installed afterwards.
Are you sure you want to continue? (Yes, No)[Yes]: yes
It has been detected that this program is executed through an SSH connection without using screen.
Continuing with the installation may lead to broken installation if the network connection fails.
It is highly recommended to abort the installation and run it inside a screen session.
Do you want to continue anyway? (Yes, No)[No]: yes
[ INFO ] Generating a temporary VNC password.
[ INFO ] Stage: Environment setup
Configuration files: []
Log file: /var/log/ovirt-hosted-engine-setup/ovirt-hosted-engine-setup-20131121170637.log
Version: otopi-1.1.1 (otopi-1.1.1-1.el6ev)
[ INFO ] Hardware supports virtualization
[ INFO ] Bridge rhevm already created
[ INFO ] Stage: Environment packages setup
[ INFO ] Stage: Programs detection
[ INFO ] Stage: Environment setup
[ INFO ] Stage: Environment customization
--== STORAGE CONFIGURATION ==--
During customization use CTRL-D to abort.
Please specify the full shared storage connection path to use (example: host:/path): myhost.home:/export
The specified storage location already contains a data domain. Is this an additional host setup (Yes, No)[Yes]? yes
[ INFO ] Installing on additional host
Please specify the Host ID [Must be integer, default: 2]:
--== SYSTEM CONFIGURATION ==--
[WARNING] A configuration file must be supplied to deploy Hosted Engine on an additional host.
The answer file may be fetched from the first host using scp.
If you do not want to download it automatically you can abort the setup answering no to the following question.
Do you want to scp the answer file from the first host? (Yes, No)[Yes]:
Please provide the FQDN or IP of the first host: 10.1.1.10
Enter 'root' user password for host 10.1.1.10:
[ INFO ] Answer file successfully downloaded
--== NETWORK CONFIGURATION ==--
The following CPU types are supported by this host:
- model_Nehalem: Intel Nehalem Family
- model_Penryn: Intel Penryn Family
- model_Conroe: Intel Conroe Family
--== HOSTED ENGINE CONFIGURATION ==--
Enter the name which will be used to identify this host inside the Administrator Portal [hosted_engine_2]:
Enter 'admin@internal' user password that will be used for accessing the Administrator Portal:
Confirm 'admin@internal' user password:
[WARNING] Failed to resolve hosted-engine.home using DNS, it can be resolved only locally
[ INFO ] Stage: Setup validation
--== CONFIGURATION PREVIEW ==--
Engine FQDN : hosted-engine.home
Bridge name : rhevm
SSH daemon port : 22
Firewall manager : iptables
Gateway address : 10.1.1.1
Host name for web application : hosted_engine_2
Host ID : 2
Image size GB : 25
Storage connection : myhost.home:/export
Console type : vnc
Memory size MB : 4096
Boot type : disk
Number of CPUs : 2
CPU Type : model_Conroe
Please confirm installation settings (Yes, No)[No]: yes
[ INFO ] Generating answer file '/etc/ovirt-hosted-engine/answers.conf'
[ INFO ] Stage: Transaction setup
[ INFO ] Stage: Misc configuration
[ INFO ] Stage: Package installation
[ INFO ] Stage: Misc configuration
[ INFO ] Configuring libvirt
[ INFO ] Generating VDSM certificates
[ INFO ] Configuring VDSM
[ INFO ] Starting vdsmd
[ INFO ] Waiting for VDSM hardware info
[ INFO ] Waiting for VDSM hardware info
[ INFO ] Connecting Storage Domain
[ INFO ] Configuring VM
[ INFO ] Updating hosted-engine configuration
[ INFO ] Stage: Transaction commit
[ INFO ] Stage: Closing up
[ INFO ] Engine replied: DB Up!Welcome to Health Status!
[ INFO ] Waiting for the host to become operational in the engine. This may take several minutes...
[ INFO ] The VDSM Host is now operational
[ INFO ] Enabling and starting HA services
Hosted Engine successfully set up
[ INFO ] Stage: Clean up
[ INFO ] Stage: Pre-termination
[ INFO ] Stage: Termination
Notes
- remember to use the same storage path you used on first host.
Migrating an existing engine
UI - operations
The host deployment may be done both using hosted-engine –deploy or ovirt-hosted-engine-setup.
Both commands are documented with man pages, so please refer to them in order to have the list of supported operations.
Configuration files
/etc/ovirt-hosted-engine/hosted-engine.confFQDN of the engine machine shared storage domainType=nfs conf=/etc/ovirt-hosted-engine/vm.conf - see below service_start_timeout vm_disk_id vmid host_id=1 for first host, more for next ones console=vnc spUUID=uuid sdUUID=uuid connectionUUID=uuid ca_cert=/etc/pki/vdsm/libvirt-spice/ca-cert.pem ca_subject=CA certificate subject vdsm_use_ssl=true gateway=ipaddress should be pingable from the host bridge=ovirtmgmt/etc/ovirt-hosted-engine/vm.confvmId memSize cpuType display devices vmName=HostedEngine spiceSecureChannels smp= number of virtual cores emulatedMachine=pc image (optional) connect iso (optional) direct lun (optional)/etc/ovirt-hosted-engine-ha/broker.conf[email] smtp-server=<address of the smtp server to send notification emails with> smtp-port=25 destination-emails=<single email address that will be used as the sender's address> source-email=<comma separated list of email addresses to send the notification emails to> [notify] # <- keys configure the list of event types we are interested in state_transition=<maintenance|start|stop|migrate|on> #^- key is event type, value is regular expression, # when it matches part of the internal detail field, the mail will be sent/etc/ovirt-hosted-engine-ha/notifications/<event type>.txt- Files in this directory are used as templates for the notification emails. The template has to contain proper email message compliant to rfc822. That means both header and body parts. Some strings are replaced by the notification engine:- {source-email} - source email address
- {destination-emails} - list of destination email addresses
- {detail} - the detail field of the event
- {hostname} - the hostname of machine that sent the event
- {time} - numeric timestamp of the message (0 = 1st of Jan 1970)
- {type} - type of the message, matches the filename
state_transition.txt ——————– From: {source-email} To: {destination-emails} Subject: ovirt-hosted-engine state transition {detail} at {hostname} The state machine changed state.
Logic
- ovirt-hosted-engine-setup executables relies on vdsClient and vdsm python API for preparing the storage infra and handling the VM.
-
create the bridge if missing
` addNetwork`
-
first check for existing pool and abort if any is found.
` getConnectedStoragePoolsList`
-
validate the specified path, checking if there’s already a domain there
` connectStorageServer
-
if a new domain has to be created, create it
` connectStorageServer
-
if a new vm image has to be created, create it
` createVolume`
-
stop the pool and start the domain monitor
` spmStop
-
run vm with installation media
` create`
-
provide spice/terminal console
` setVmTicket`
- wait for os to be installed and then reboot
- start again the VM as before
- wait for engine to be installed
- polling on liveliness till engine is up
- add host without rebooting it.
- wait for the host to be operational
- hand over the VM to the HA daemons (shutdown the VM and start daemons which will take care now of the VM)
Enhancements
- sanlock vm/host id broker
- shared cluster config
- shared vm config
- engine to reflect the host running the engine VM
- engine to reserve resources for the engine VM
Open issues
- pool connection is needed to run vm (should be solved on vdsm level) - we can’t connect two pools to vdsm
- sanlock on vm image (should be solved on vdsm level) - we can workaround for now
- vdsm sanity for running a VM from another pool
- vdsm providing monitoring service for tasks
- change bridge details
- host level oprations on engine hypervisor
Limitations
- NFS FS only (Gluster and Block to be supported at a later stage)
- RHEV-H not supported
- Only one VM is deployed and managed by HA daemons (support for additional VMs to be added at a later stage).
Operational Routine
Phase 2: engine vm high availability daemon
- Daemon setup: The HA daemon is deployed as an rpm package (preinstalled on ovirt-node).
- The daemon maintains two conf files: one is local and contains the NFS mount details, the other is on the NFS mount and it contains the network health check IPs and the engine vm ip (additional configs go here).
- The daemon starts on all the configured hosts, and there it will start maintaining the engine VM. The Detailed Feature page will have a flow chart of how exactly the daemon operates
HA daemon requirements during normal ops:
- Monitor the state of the Engine VM and restart the VM on other hosts in case of failure
- Monitor the Engine status in the VM and restart the VM (or just the engine service - probably in the future versions) if it fails
- Monitor the status of the host that is currently running the Engine VM, live migrate the engine in case of host health degradation (network/storage loss)
Issues to address specifically:
- Engine VM Host losing only the management network - move the engine to another host
- All the management network is down for all hosts - do nothing, no point taking the engine down if it can’t operate anywhere
- Hypervisor crash - restart the engine on another host
- Engine VM crashing - restart locally, if fails - on another host
- Engine service unavailable - restart VM after a timeout, if that fails - alert
- Engine VM storage down - restart the engine on another host
- A situation when the host where the Egnine is running is in a problematic state, while the Engine VM is still up should also trigger a failover, or live migration.
- Avoid race conditions in case of a multiple host start - e.g. many hosts not detecting the engine VM and trying to start it
- SBA for the engine VM should be provided (is sanlock enough?)
Additional functionality required at host level
- Heartbeat the Engine VM status
- Heartbeat the Engine service health
- Heartbeat the current Engine VM host
- Host self monitoring (HB to the Engine, designated network entities)
- Inter-host selection for the next host to pick up the Engine VM, with host priorities in place
- Host failure counter, that will have effect on the host selection heuristics
- (optional) Host capabilities (minimal CPU/RAM available) will have effect on the host selection heuristics
Nice to have
- Ability to tolerate a file share loss: have a mirrored copy of the Engine VM disk on another share
Required modifications
- VDSM currently only support volume locking on the global level only - thus it can be currently either globally on or off, with no option to enable it for specific VM only.
- In VDSM handling of operations like live snapshot (hoplug the new volume lease), live storage migration (hotplug all the new volume leases on the new storage and hotunplug all the old ones), disk hotplug/hotunplug (hotplug/hotunplug the volume lease), etc. must be handled properly (currently these cases are not handled).
- VDSM is currently limited to only one Storage Pool, thus it’s currently impossible to store the Engine VM not in the same Storage Pool as other VMs that will be managed.
Agent State Diagram
FSM diagram for hosted engine agent states (generated from README.AGENT-FSM.gv in agent source tree): 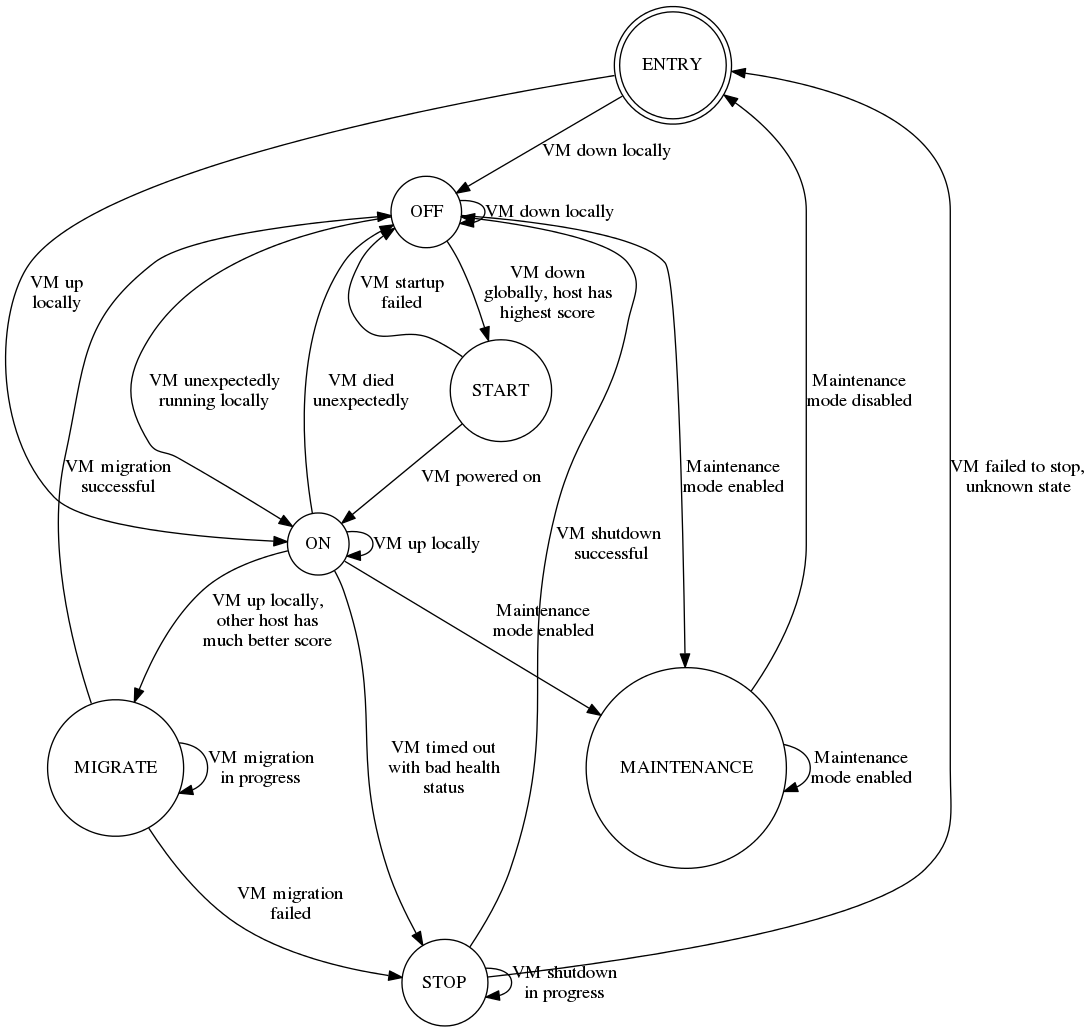
Maintenance Flows
The HA Agent will support 2 types of maintenance:
- Global maintenance: all HA agents in the cluster will ignore the engine VM state while this mode is enabled, allowing an administrator to start/stop/modify the engine VM without any worry of interference from the HA agents. To accomplish this, a flag will be written to the HA metadata residing on shared storage, and all HA agents will heed this flag and enter a mode where the only actions they take will be to a) remain initialized, b) update their scores, and c) watch for the flag to become unset. Once the flag is unset, the agents will discover the status of the VM as they do upon starting up, and then will resume normal operation.
- Local maintenance: an individual HA agent will stop the VM and not attempt to restart it while this mode is enabled, in an effort to allow the local host to enter maintenance mode (in vdsm/engine). Another host in the cluster should attempt to start the engine VM, at which time maintenance operations on the first host can proceed. A shortcut to initiate this process is to shut down the engine VM manually, as any unexpected shutdown of the VM on a given host will cause the HA agent on that host to temporarily drop its score to 0. In this event, the administrator should still log into the host and enter maintenance mode to ensure the score does not recover, possibly causing the host to reacquire the engine VM. Once local maintenance mode is disabled, the score on this host will recover and the agent will resume normal operation.